HEPATOPROTECTIVE ACTIVITY OF HYDROETHANOL EXTRACT OF CURCUMA LONGA LINN. ON PARACETAMOL AND CARBON TETRACHLORIDE-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY IN RATS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/acs.v10i2.208Keywords:
Hepatoprotective, Curcuma Longa, Paracetamol, Carbon tetrachloride, Liver function biomarkers, HistopathologyAbstract
Background: Curcuma longa Linn. is extensively used for its culinary and ethnomedicinal properties, which include claims of prevention and treatment of hepatic diseases. However, there are limited studies on the effectiveness of C. longa on drug and chemically-induced hepatotoxicity; thus, we evaluated the anti-hepatotoxic effects of doses of the hydroethanol extract of C. longa L. (HECL) using Paracetamol (PCM) and Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) models.
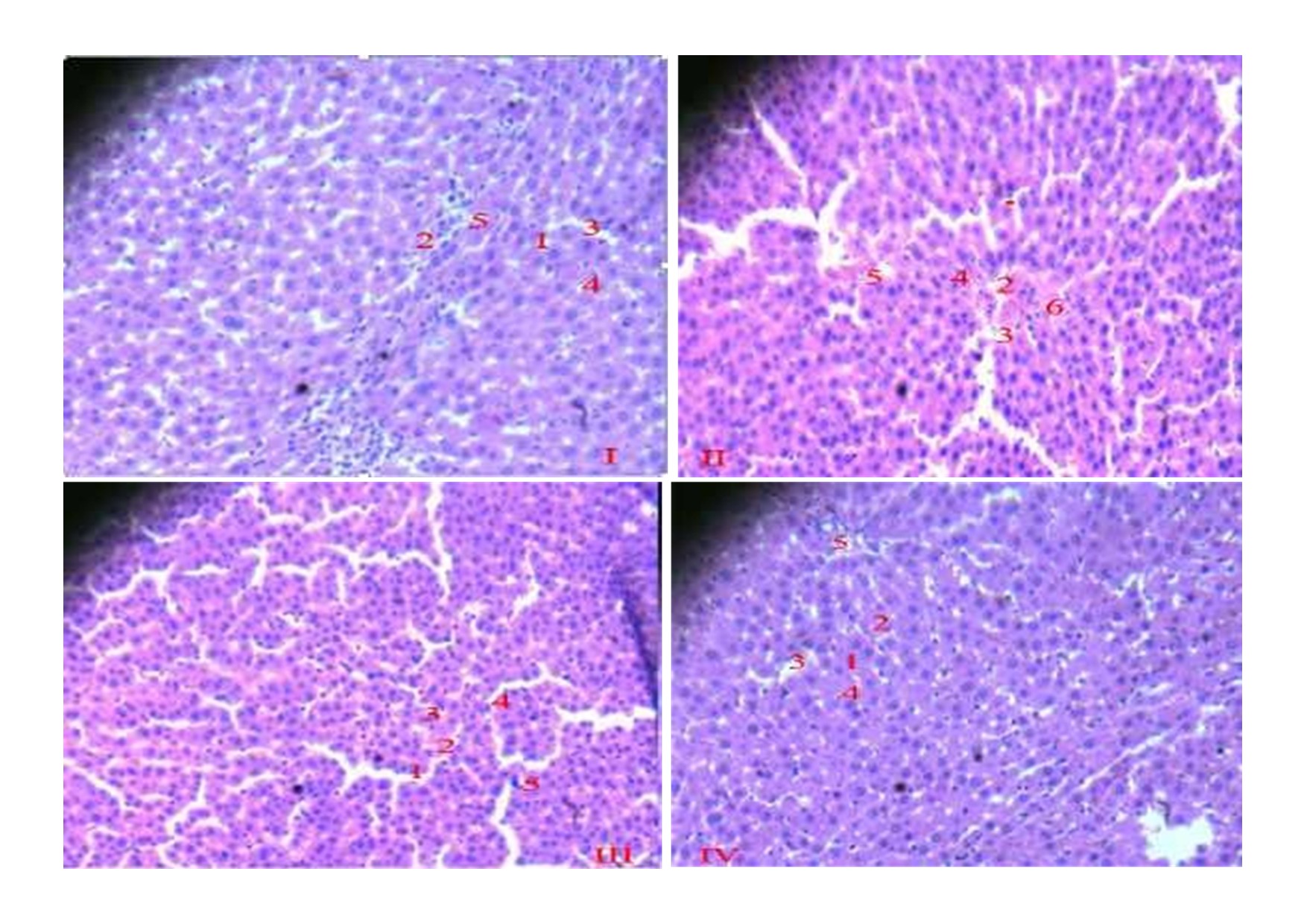
Methodology: This study was conducted on forty rats randomly divided into PCM and CCl4 models of four study groups each (n=5). For the PCM model, Group I: Normal saline (NS, 10 ml/kg, p.o. ); Group II: PCM (600 mg/kg, p.o.) & 3 ml/kg NS; Group III & IV: PCM & HECL (200 & 400 mg/kg, respectively, p.o.); while the CCl4 model, Group V: Olive oil (10 ml/kg, i.p.); Group VI: CCl4 (15 ml/kg. of 20% v/v, i.p.) & olive oil; Group VII & VIII: CCl4 & HECL (100 & 300 mg/kg, respectively, p.o.). HECL was administered at 2, 6, and 10 h post-induction. Following euthanizing, blood samples were collected for liver function tests: Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and uric acid levels were measured, while liver was excised for histopathology was assessed via hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Results: In the PCM model, HECL (200 and 400 mg/kg) significantly reduced ALT and uric acid (p<0.05), with 400 mg/kg showing superior efficacy. AST reductions were non-significant. In the CCl4 model, CCl4 significantly increased ALT, AST, and uric acid (p<0.05). HECL (100 and 300 mg/kg) significantly lowered these biomarkers (p<0.05), with 300 mg/kg more effective.
Conclusions: HECL elicited remarkable hepatoprotective effects, likely due to apoptotic restoration and cytosolic restoration, thereby supporting its use in ethnomedicine for prevention and treatment of liver diseases.