URIC ACID AND OTHER RISK FACTORS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS IN SOUTHERN PART OF NIGERIA
Uric Acid in Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
ABSTRACT
Background: There is an increased prevalence of hypertension especially in low and middle-income countries. Hyperuricaemia is linked with an increased risk for hypertension, independent of typical risk factors of hypertension. Also, serum uric acid concentrations have been linked with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. This study was aimed at evaluating the serum uric acid levels in hypertensive patients and comparing it with other risk factors of cardiovascular disease.
Methodology: This was a hospital-based cross-sectional study carried out between October 2022 and December 2023 at the Delta State Central Hospital, Warri. The study included 200 participants with hypertension and 100 healthy controls.
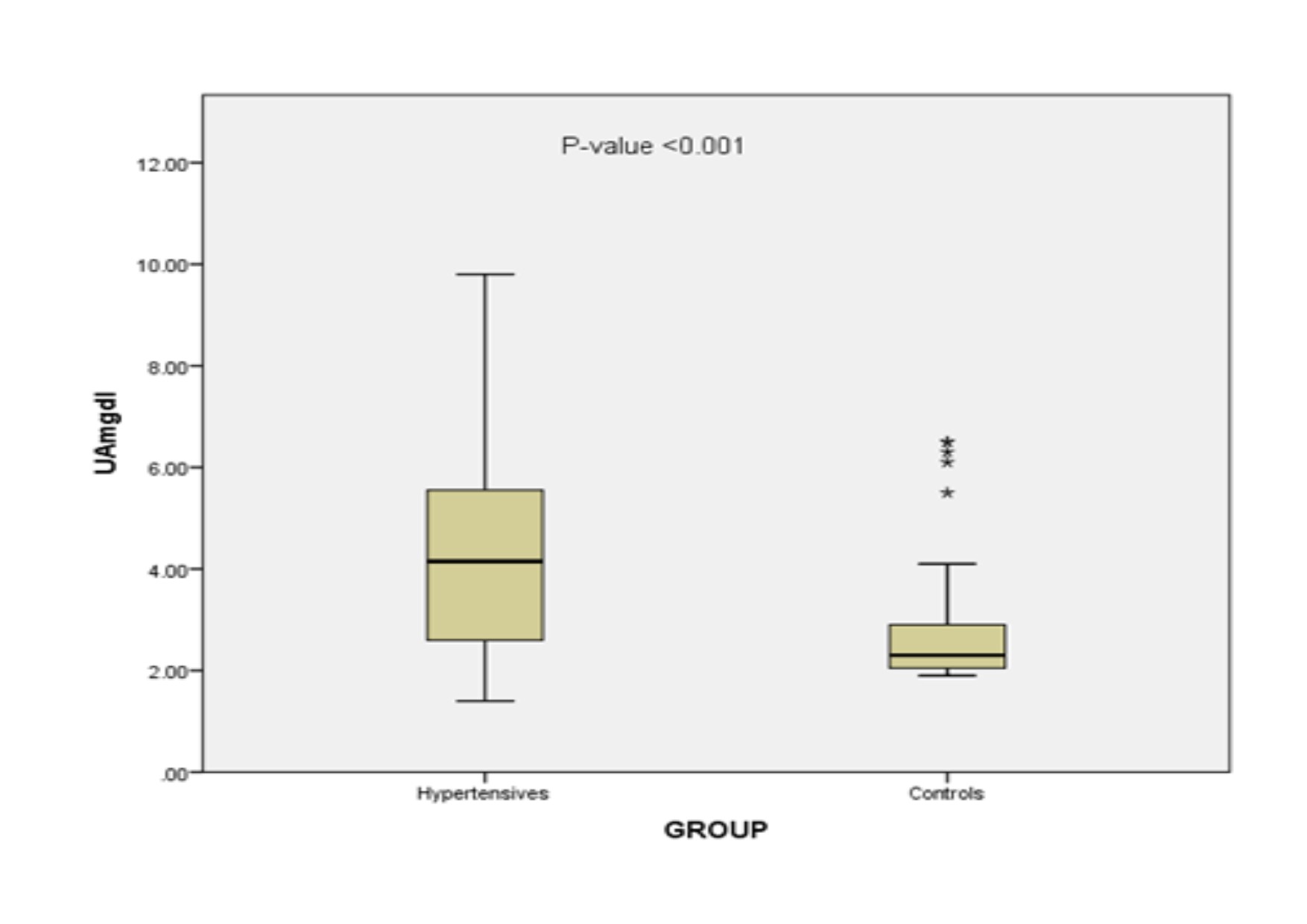
Results: Uric acid level ranged from 0.08 – 0.58 mmol/L in the hypertensives with a mean of 0.24 ± 0.11 mmol/L. In the controls, the mean value was 0.16 ± 0.07 mmol/L. The difference in mean was statistically significant (p < 0.001). Forty-two (21.0%) of the hypertensives compared to 5 (5.0%) of the controls had hyperuricaemia (p = 0.005). In the hypertensives, uric acid correlated positively with BMI (r = 0.330, p = 0.001) and weight circumference (r = 0.263, p = 0.003). Similarly, in the controls, there was a positive correlation between uric acid level and BMI (r = 0.458, 0.001).
Conclusion: Serum uric acid levels were significantly higher in the hypertensive patients than in the normotensive controls. There was a significant positive correlation between uric acid and BMI and WC in the hypertensive population and a significant positive correlation between uric acid and BMI in the controls.
Keywords: Hypertension. Uric acid, body mass index, estimated glomerular filtration rate, waist circumference.