EVALUATION OF ADVANCED HIV STAGING AND CARDIAC TROPONIN I AS PREDICTORS OF ACQUIRED HEART DISEASES: A PROSPECTIVE CASE CONTROL STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR SYSTOLIC AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION AMONG CHILDREN IN ILORIN NIGERIA
Abstract
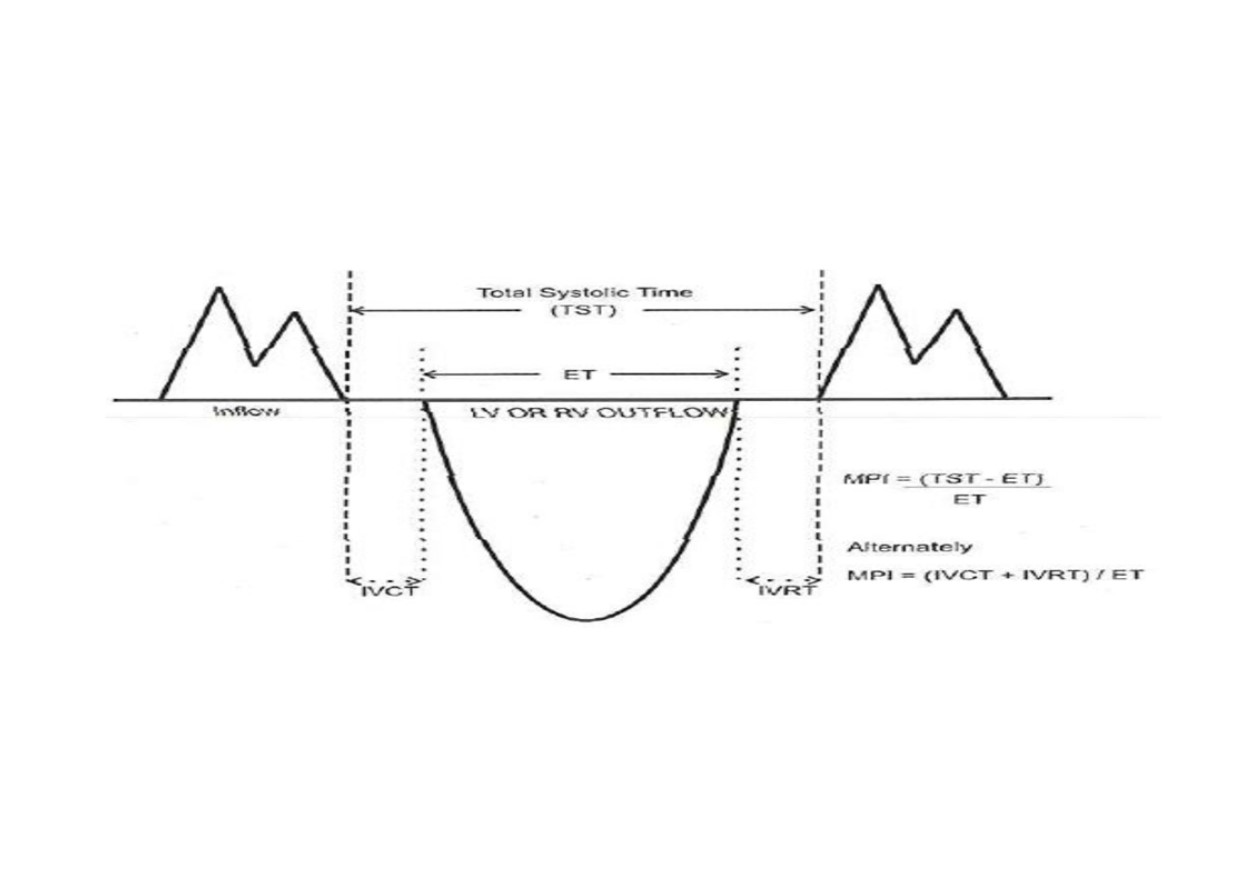
Background: Left ventricular dysfunction consists of the systolic and diastolic components. The gold standard for assessing this important cardiac function is echocardiography. The performance of echocardiography is limited by the high cost of the equipment, the technical know-how required, and its affordability, especially in developing countries. This study determined the predictive factors of left ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction among children at a tertiary health facility in Ilorin, Nigeria.
Methodology: A prospective case-control study of subjects with left ventricular systolic and/or diastolic dysfunction recruited consecutively through the Paediatric Cardiology Clinic and an equally matched control using echocardiography over a 4-month period. HIV screening was done. Serum cardiac troponin I (cTnI) was assessed, and data was analysed with SPSS® v 20, presented as tables or graphs. Multivariate logistic regression was done to determine the predictors of left ventricular dysfunction. The predictive performance and accuracy of cTnI were determined by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. A significant p is < 0.05.
Results: A total of 200 subjects (and controls) were studied. There was a significant association between myocardial injury (raised cTnI) and left ventricular dysfunction (p < 0.001). Most of the subjects with myocardial injuries have left ventricular dysfunction. Raised serum cTnI and the advanced stage of HIV are good predictors of left ventricular dysfunction.
Conclusions: There was a significant association between raised cTnI and left ventricular dysfunction. Immunosuppression and elevated cTnI are predictors of left ventricular dysfunction. Routine screening of children with raised cTnI and advanced HIV for left ventricular dysfunction using echocardiography is recommended.